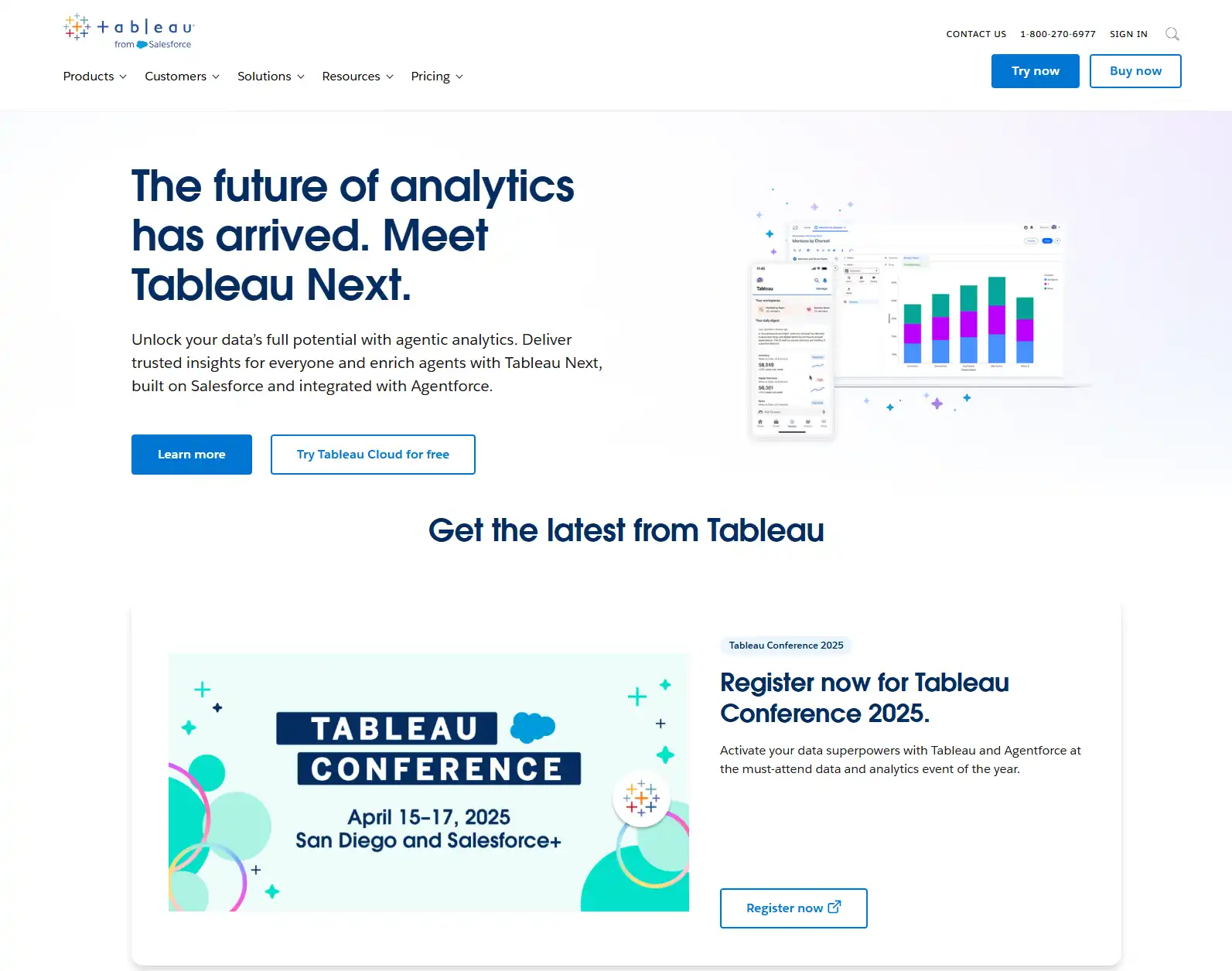
Tableau transforms complex data into intuitive visualizations, helping businesses make data-driven decisions through interactive dashboards and analytics.
Organizations are drowning in information but starving for insights. You’ve probably found yourself staring at spreadsheets, wondering how to transform those endless rows and columns into meaningful business decisions. If you’re struggling to make sense of your data or communicate findings effectively to stakeholders, you’re not alone. That’s where powerful data visualization tools like Tableau enter the picture, promising to bridge the gap between data and understanding.
Introduction to Tableau
What is Tableau and its Purpose?
Tableau is a leading data visualization and business intelligence platform designed to help people see and understand their data. Unlike traditional reporting tools, Tableau specializes in interactive, visual analytics that enables users to explore data without extensive technical skills.
At its core, Tableau’s purpose is to make data analysis more accessible, allowing businesses to uncover hidden patterns, identify emerging trends, and make data-driven decisions. The platform connects to nearly any data source—from basic Excel spreadsheets to complex databases and cloud services—transforming raw numbers into intuitive visualizations that reveal the stories behind the data.
Tableau follows a “show me, don’t tell me” philosophy, emphasizing visual representation over complex calculations. This approach democratizes data analysis, putting powerful analytical capabilities in the hands of business users, not just data scientists or IT professionals.
Who is Tableau Designed For?
Tableau caters to a diverse audience across various roles and industries:
- Business Analysts and Data Professionals: Those who work with data daily benefit from Tableau’s ability to quickly explore information and create compelling visualizations.
- Executives and Decision-Makers: Leaders use Tableau dashboards to monitor key metrics and make informed strategic decisions.
- Data Scientists: Despite its user-friendly interface, Tableau offers advanced analytics capabilities that data scientists can leverage alongside traditional tools.
- IT Professionals: IT teams appreciate Tableau’s governance features and ability to integrate with existing data infrastructure.
- Organizations across industries: From healthcare and finance to retail and education, Tableau serves diverse sectors. Whether you’re analyzing patient outcomes, financial portfolios, sales performance, or student achievement, Tableau adapts to specific industry needs.
The platform scales from individual analysts exploring data on their desktops to enterprise-wide deployments with thousands of users accessing governed data sources through browsers and mobile devices.
Getting Started with Tableau: How to Use It
Getting up and running with Tableau involves a few straightforward steps:
- Choose the right Tableau product: Tableau offers several products including Tableau Desktop (for individual analysis), Tableau Server (for sharing within organizations), Tableau Online (cloud-based hosting), and Tableau Public (free for publicly shared visualizations).
- Download and install: For desktop products, download and install the software from Tableau’s website. Web-based versions require only a browser.
- Connect to data: Launch Tableau and connect to your data source. Tableau supports connections to:
- Files (Excel, CSV, JSON)
- Relational databases (SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL)
- Cloud applications (Salesforce, Google Analytics)
- Big data platforms (Hadoop, Amazon Redshift)
- Build your first visualization: Tableau’s drag-and-drop interface makes it easy to create charts and graphs. Simply:
- Drag fields from the data pane to the rows and columns shelves
- Select visualization types from the “Show Me” panel
- Add filters, colors, and interactive elements
- Create a dashboard: Combine multiple visualizations into interactive dashboards by:
- Selecting “Dashboard” from the navigation
- Dragging worksheets onto the canvas
- Adding interactive filters and actions
- Share your insights: Depending on your Tableau product, publish to Tableau Server, Tableau Online, or Tableau Public to share with others.
For beginners, Tableau offers extensive free training resources, including video tutorials, live webinars, and a supportive community forum where users can ask questions and share ideas.
Tableau’s Key Features and Benefits
Core Functionalities of Tableau
Tableau’s strength lies in its comprehensive set of data visualization and analysis capabilities:
1. Visual Analytics
- Drag-and-drop interface for creating visualizations
- “Show Me” feature suggesting optimal chart types
- VizQL technology that translates drag-and-drop actions into database queries
2. Data Connection and Preparation
- Native connectors to 80+ data sources
- Live connection or in-memory extraction options
- Data preparation tools for cleaning and transforming data
- Data modeling capabilities including joins and blends
3. Advanced Analytics
- Built-in statistical functions
- Trend lines and forecasting
- Clustering and segmentation
- Integration with R, Python, and MATLAB
4. Dashboarding and Storytelling
- Interactive dashboard creation
- Parameter controls for “what-if” analysis
- Story Points feature for guided data narratives
- Device-specific layouts for mobile optimization
5. Enterprise Features
- Row-level security and user permissions
- Metadata management and data governance
- Scheduling and subscription options
- APIs for embedding and extending functionality
Advantages of Using Tableau
Tableau offers numerous benefits that explain its popularity among data professionals:
🚀 Speed to Insight
Tableau dramatically reduces the time between question and answer. With its intuitive interface, users can quickly explore data, test hypotheses, and uncover insights that might otherwise remain hidden in spreadsheets or databases.
👥 Democratized Analysis
By lowering the technical barriers to data analysis, Tableau enables more people within an organization to work with data. This democratization creates a data culture where decisions at all levels are informed by evidence rather than intuition.
🔄 Flexibility and Adaptability
Whether you’re working with gigabytes of historical data or streaming real-time metrics, Tableau adapts to your needs. The platform handles various data types, sizes, and sources, providing flexibility as your requirements evolve.
🔎 Self-Service Analytics
Tableau reduces dependency on IT or data specialists for routine analysis. Business users can answer their own questions without submitting report requests and waiting for results, leading to faster and more agile decision-making.
📊 Powerful Visualization
Humans are visual creatures, and Tableau leverages this by transforming complex data into intuitive visualizations. These visuals make patterns and outliers immediately apparent, facilitating quicker understanding and more effective communication.
🔗 Collaboration and Sharing
Tableau’s sharing capabilities facilitate knowledge transfer across organizations. Dashboards and insights can be distributed to stakeholders, fostering a common understanding of key metrics and trends.
Main Use Cases and Applications
Tableau excels across various use cases, including:
Business Intelligence and Reporting
Tableau serves as a modern BI platform for organizations, providing dynamic dashboards that replace static reports. Users track KPIs, analyze performance metrics, and distribute insights across departments.
Sales and Marketing Analytics
Marketing teams leverage Tableau to:
- Analyze campaign performance
- Track customer acquisition costs
- Visualize customer journey metrics
- Identify high-value customer segments
- Optimize channel attribution
Financial Analysis
Financial professionals use Tableau for:
- Budget variance analysis
- Cash flow monitoring
- Investment portfolio visualization
- Risk assessment
- Financial forecasting
Supply Chain Optimization
Supply chain managers gain visibility into:
- Inventory levels across locations
- Supplier performance metrics
- Logistics and transportation costs
- Demand forecasting
- Production bottlenecks
Healthcare Analytics
Healthcare organizations apply Tableau to:
- Patient outcome analysis
- Resource utilization tracking
- Population health management
- Claims analysis
- Compliance monitoring
HR and Workforce Analytics
HR departments leverage Tableau for:
- Turnover analysis and prediction
- Recruitment funnel visualization
- Compensation benchmarking
- Training effectiveness measurement
- Diversity and inclusion metrics
Exploring Tableau’s Platform and Interface
User Interface and User Experience
Tableau’s interface strikes a balance between power and usability, making it accessible to newcomers while offering depth for experienced users.
Workspace Layout
The main Tableau Desktop interface includes:
- Data pane: Lists all available fields from connected data sources
- Shelves and cards: Areas where you place fields to build visualizations (rows, columns, filters, etc.)
- Canvas: Central area displaying the current visualization
- Show Me panel: Suggests visualization types based on selected fields
- Toolbar: Contains common actions and formatting tools
- Sheets tabs: For navigating between worksheets, dashboards, and stories
Visualization Building Process
Creating visualizations in Tableau follows an intuitive flow:
- Connect to data and prepare it for analysis
- Drag dimensions (categorical fields) and measures (numerical fields) to the canvas
- Choose visualization types or let Tableau recommend options
- Add context with filters, parameters, and calculated fields
- Enhance with colors, tooltips, and formatting
- Combine into dashboards for a comprehensive view
User Experience Considerations
Tableau prioritizes user experience through:
- Progressive disclosure of advanced features
- Consistent design patterns across products
- Context-sensitive help and tooltips
- Real-time visual feedback when building charts
- Performance optimization for large datasets
The interface encourages exploration and iteration, allowing users to rapidly test different visualization approaches until they find the most effective way to present their data.
Platform Accessibility
Tableau offers various ways to access and interact with the platform, accommodating different user needs and technical environments.
Desktop vs. Web Experience
- Tableau Desktop: Full-featured desktop application for Windows and Mac, offering the most comprehensive development environment
- Tableau Web Authoring: Browser-based creation and editing capabilities, available through Tableau Server or Tableau Online
- Tableau Mobile: Native iOS and Android apps optimized for on-the-go data consumption
Accessibility Features
Tableau has increased its focus on accessibility, implementing features such as:
- Screen reader compatibility
- Keyboard navigation
- Color vision deficiency palettes
- Alt text for visualizations
- Accessible authoring guidelines
Language Support
Tableau’s interface is available in multiple languages, including:
- English
- French
- German
- Spanish
- Japanese
- Chinese (Simplified and Traditional)
- Portuguese
- Korean
- Italian
This internationalization makes Tableau accessible to global teams, although created content may require separate localization.
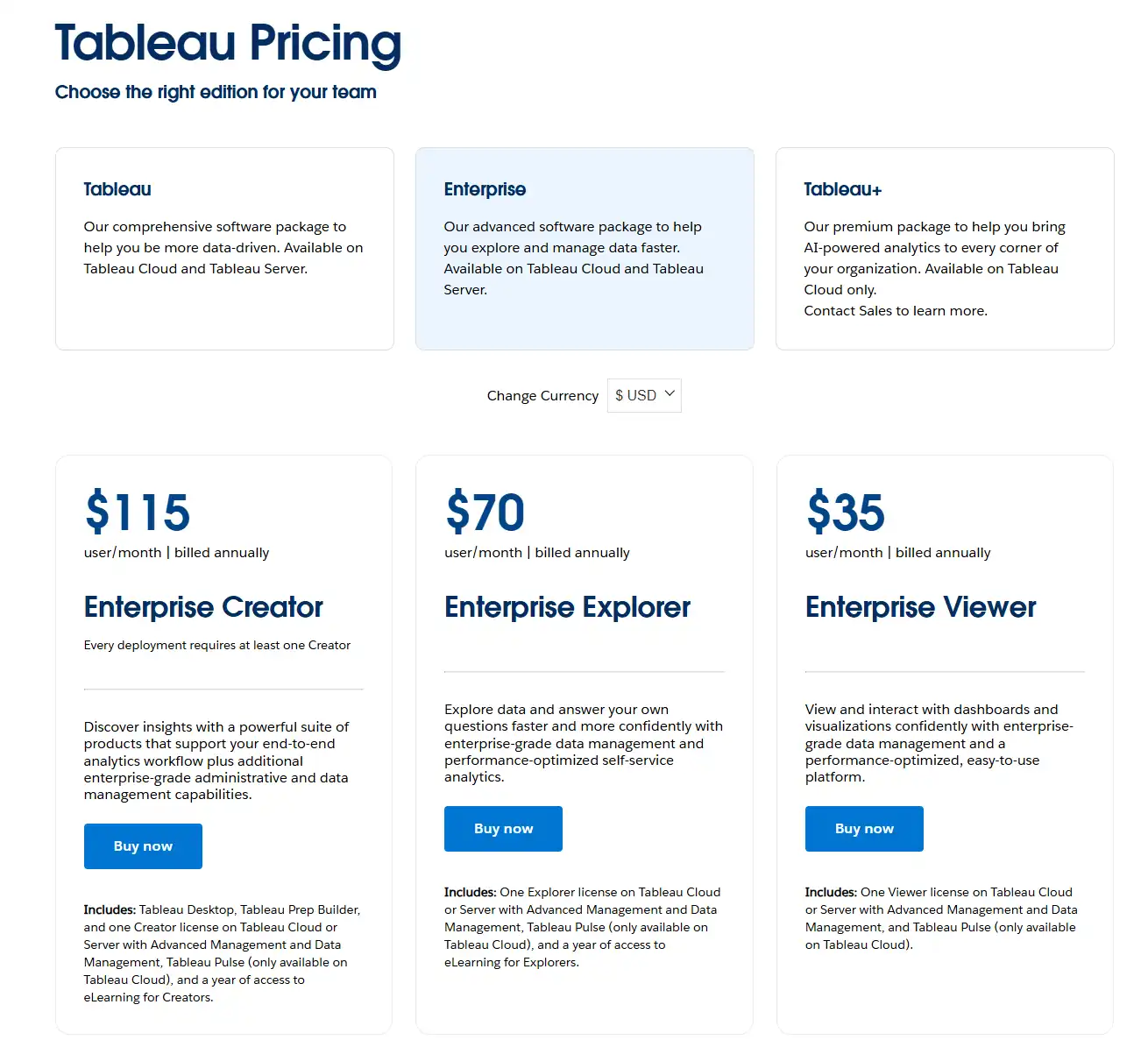
Tableau Pricing and Plans
Subscription Options
Tableau offers a tiered pricing model with different products tailored to various user roles and requirements:
| Product | Target Users | Key Capabilities | Annual Price (per user) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tableau Creator | Analysts & power users | Full authoring capabilities, data connection, desktop & web | $70/month billed annually |
| Tableau Explorer | Business users who need self-service analytics | Web authoring, exploration of governed data sources | $42/month billed annually |
| Tableau Viewer | Content consumers | View and interact with dashboards | $15/month billed annually |
These user types can be deployed on:
Tableau Server
- On-premises or private cloud deployment
- Complete control over your environment
- Additional infrastructure costs
- One-time license fee plus annual maintenance
Tableau Online
- Fully hosted SaaS solution
- No infrastructure to maintain
- Automatic updates
- Slightly higher per-user cost than Tableau Server
Tableau Public
- Free service for publicly sharing visualizations
- No private or sensitive data
- All content is accessible to anyone on the web
Tableau Embedded
- For integrating Tableau analytics into applications
- Custom pricing based on deployment size
For organizations just getting started, Tableau offers various promotional pricing and special programs for nonprofits, educational institutions, and students.
Free vs. Paid Features
Tableau offers both free and paid options with significant differences in capabilities:
Tableau Public (Free)
✅ Full visualization capabilities
✅ Public sharing of workbooks
✅ 10GB storage per user
✅ Access to Tableau Public gallery for inspiration
❌ No private data storage or sharing
❌ Limited data connection options
❌ No scheduled refreshes
❌ Cannot save work locally
Tableau Desktop (Paid)
✅ All visualization capabilities
✅ Connect to 80+ data sources
✅ Private and secure sharing options
✅ Local saving and file management
✅ Data preparation tools
✅ Advanced analytics features
✅ Integration with R and Python
Tableau Trial Options
Tableau offers a 14-day free trial of Tableau Desktop for users who want to explore the full capabilities before committing to a purchase.
Tableau Reviews and User Feedback
Pros and Cons of Tableau
Based on user reviews and expert analysis, here’s a balanced overview of Tableau’s strengths and limitations:
Pros:
- Visualization Excellence: Users consistently praise Tableau’s visualization capabilities, citing the intuitive creation process and professional results.
- Connectivity Options: The ability to connect to almost any data source receives high marks, with users appreciating the flexibility.
- Community Support: Tableau’s active user community is frequently mentioned as a valuable resource for learning and problem-solving.
- Regular Innovation: Quarterly updates introduce new features and improvements, keeping the platform current with evolving analytics needs.
- Scalability: Organizations appreciate how Tableau grows with them, from individual use to enterprise deployment.
Cons:
- Learning Curve: While basic features are accessible, mastering advanced capabilities requires time and dedication.
- Cost: Small organizations and individual users often mention pricing as a barrier, particularly compared to some alternatives.
- Performance with Large Datasets: Some users report performance challenges when working with extremely large datasets, though this has improved in recent versions.
- Limited ETL Capabilities: While Tableau Prep has enhanced data preparation features, some users find it less robust than dedicated ETL tools.
- Mobile Experience: While improved, the mobile experience isn’t as comprehensive as the desktop version.
User Testimonials and Opinions
Here’s what real users are saying about their Tableau experience:
“Tableau transformed how our marketing team approaches campaigns. What used to take days of analysis now happens in real-time. We can see what’s working and pivot quickly when something isn’t performing.”
– Marketing Director, Retail Industry
“The learning curve was steeper than expected, but the payoff has been worth it. Our executive dashboards give leadership a clear picture of operations across 12 facilities, and they can drill down when they need more detail.”
– Business Intelligence Analyst, Healthcare
“We evaluated several BI tools, and Tableau won for its balance of power and usability. Two years in, we’ve deployed it to over 500 users across finance, operations, and sales. The consistent interface means people can move between departments and still understand the dashboards.”
– Enterprise Architect, Manufacturing
“Tableau licensing costs add up quickly as you scale. We’ve had to be strategic about who gets Creator licenses versus Viewers. That said, the ROI has been clear in terms of better decision-making and time saved.”
– IT Director, Financial Services
According to G2, a leading business software review platform, Tableau maintains a 4.3/5 rating based on over 1,500 reviews. Gartner consistently positions Tableau as a Leader in its Magic Quadrant for Analytics and Business Intelligence Platforms.
Tableau Company and Background Information
About the Company Behind Tableau
Tableau Software was founded in 2003 by Chris Stolte, Pat Hanrahan, and Christian Chabot at Stanford University. The company emerged from groundbreaking research in visualization techniques for exploring and analyzing relational databases.
Key Company Milestones:
- 2003: Tableau Software founded
- 2004: First product, Tableau Desktop, released
- 2007: Tableau Server introduced for enterprise deployment
- 2010: Tableau Public launched as a free service
- 2013: Initial public offering (IPO) on the New York Stock Exchange
- 2019: Acquired by Salesforce for $15.7 billion
- 2021: Tableau Exchange launched to expand the ecosystem with partner solutions
Tableau as Part of Salesforce
Since the 2019 acquisition, Tableau has operated as part of Salesforce but maintains its distinct brand and product identity. The integration has brought several advantages:
- Enhanced integration with Salesforce CRM data
- Access to Salesforce’s global sales channels and customer base
- Integration with Salesforce Einstein for advanced AI capabilities
- Investment in accelerated product development
Under Salesforce’s umbrella, Tableau continues to focus on its mission of helping people see and understand data, while benefiting from the resources of one of the world’s largest enterprise software companies.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Tableau maintains a strong commitment to social impact through its Tableau Foundation, which has committed to donating $100 million in software, training, and grants by 2025. Key initiatives include:
- Data literacy education programs
- Supporting data-driven approaches to global health challenges
- Environmental conservation efforts
- Equity-focused initiatives in underserved communities
The company also promotes sustainable business practices and maintains a diverse and inclusive workplace culture.
Tableau Alternatives and Competitors
Top Tableau Alternatives in the Market
While Tableau leads the data visualization space, several alternatives offer compelling features for different needs and budgets:
1. Microsoft Power BI
Power BI
- Strengths: Deep Microsoft ecosystem integration, attractive pricing, frequent updates
- Best for: Organizations heavily invested in Microsoft tools, budget-conscious teams
- Pricing: Free limited version; Power BI Pro from $9.99/user/month
2. Qlik Sense
Qlik Sense
- Strengths: Associative engine for data discovery, strong data governance
- Best for: Large enterprises, organizations with complex data relationships
- Pricing: Business starts at $30/user/month; Enterprise has custom pricing
3. Looker (Google Cloud)
Looker
- Strengths: SQL-based approach, modeling layer, embedded analytics
- Best for: Companies with strong SQL skills, Google Cloud users
- Pricing: Custom pricing based on deployment
4. Domo
Domo
- Strengths: Cloud-native platform, strong mobile experience, data integration
- Best for: Organizations seeking an all-in-one cloud BI platform
- Pricing: Starts around $83/user/month, with custom enterprise pricing
5. Sisense
Sisense
- Strengths: Handling complex data, embedded analytics, AI capabilities
- Best for: Technical users, organizations embedding analytics in products
- Pricing: Custom pricing based on deployment
6. ThoughtSpot
ThoughtSpot
- Strengths: Search-based interface, AI-driven analytics
- Best for: Organizations seeking Google-like search for their data
- Pricing: Custom pricing based on deployment scale
Tableau vs. Competitors: A Comparative Analysis
Let’s compare Tableau with two of its primary competitors on key factors:
Tableau vs. Power BI
| Factor | Tableau | Power BI |
|---|---|---|
| Visualization Capabilities | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Exceptional flexibility and design options | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Strong with consistent improvement |
| Ease of Use | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Intuitive for visualization, steeper for advanced features | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ User-friendly for Microsoft users |
| Data Connectivity | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Extensive native connectors | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Strong, especially for Microsoft sources |
| Performance | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Very good with large datasets | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Comparable performance |
| Mobile Experience | ⭐⭐⭐ Functional but not a primary strength | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Strong mobile apps |
| Enterprise Features | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Comprehensive governance and security | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Excellent Microsoft ecosystem integration |
| Cost | ⭐⭐⭐ Higher investment, especially at scale | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ More affordable, especially with E5 licenses |
Tableau vs. Qlik Sense
| Factor | Tableau | Qlik Sense |
|---|---|---|
| Data Exploration | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Excellent for visual exploration | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Associative engine excels at discovery |
| Learning Curve | ⭐⭐⭐ Moderate learning curve | ⭐⭐ Steeper learning curve |
| Visualization Types | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Extensive built-in options | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Strong but not as extensive |
| Scalability | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Handles enterprise needs well | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Excellent for very large deployments |
| Data Preparation | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Improving with Tableau Prep | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Strong built-in ETL capabilities |
| Community Support | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Largest user community | ⭐⭐⭐ Active but smaller community |
| Scripting/Extensions | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Good R and Python integration | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Strong with open APIs |
When choosing between Tableau and alternatives, consider your organization’s:
- Existing technology investments
- User technical proficiency
- Budget constraints
- Specific visualization needs
- Scale of deployment
- Data complexity
Many organizations actually maintain multiple BI tools for different use cases, with Tableau often serving as the premium visualization layer atop a broader analytics infrastructure.
Tableau Website Traffic and Analytics
Website Visits Over Time
Tableau.com consistently ranks among the most visited business intelligence websites globally. According to SimilarWeb data, the site typically receives between 4-6 million monthly visits, with notable traffic spikes during major product releases and annual conferences.
Quarterly Traffic Trends (2022-2023):
- Q1 2022: ~4.8M monthly visits
- Q2 2022: ~5.2M monthly visits
- Q3 2022: ~5.0M monthly visits
- Q4 2022: ~5.5M monthly visits
- Q1 2023: ~5.7M monthly visits
This steady growth reflects increasing interest in data visualization solutions and Tableau’s market position. The Tableau Public gallery, which showcases community-created visualizations, contributes significantly to this traffic.
Geographical Distribution of Users
Tableau’s user base spans the globe, with particularly strong presence in:
- United States (35% of traffic)
- India (12%)
- United Kingdom (6%)
- Canada (4%)
- Germany (3%)
- Australia (3%)
- Japan (2.5%)
- France (2.5%)
- Brazil (2%)
- Singapore (1.5%)
This distribution aligns with global IT spending patterns and markets where data-driven decision making is most mature. The strong presence in India reflects both enterprise adoption and the country’s large technical workforce.
Main Traffic Sources
Tableau attracts visitors through diverse channels:
Traffic Source Breakdown:
- Organic Search: 55% (dominated by product-related queries and educational content)
- Direct Traffic: 22% (indicating strong brand recognition)
- Referral Traffic: 12% (from technology partners, review sites, and educational institutions)
- Social Media: 6% (primarily LinkedIn and Twitter)
- Email Marketing: 4%
- Paid Search: 1%
The high percentage of organic traffic demonstrates Tableau’s strong content marketing strategy, with the company regularly publishing educational resources, whitepapers, and industry reports that attract potential users seeking data visualization solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions about Tableau (FAQs)
General Questions about Tableau
What is Tableau used for?
Tableau is used for transforming raw data into interactive visualizations, dashboards, and reports that make it easier to understand patterns, trends, and insights within data. Organizations use it for business intelligence, data analysis, and communicating findings to stakeholders.
Is Tableau difficult to learn?
Tableau is designed to be user-friendly. Basic functions like creating simple charts can be learned in a few hours. Mastering advanced features typically takes a few weeks of regular use. Tableau offers extensive free training resources to accelerate the learning process.
Do I need coding skills to use Tableau?
No coding is required for most Tableau functions. The drag-and-drop interface allows users to create visualizations without programming. However, knowledge of calculation syntax (similar to Excel formulas) is helpful for advanced analysis, and optional integrations with R, Python, or SQL can extend functionality.
What types of data can Tableau connect to?
Tableau connects to virtually any data source, including:
- Spreadsheets (Excel, CSV)
- Databases (SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL)
- Cloud services (Salesforce, Google Analytics)
- Big data platforms (Hadoop, Amazon Redshift)
- Statistical files (SAS, SPSS)
- Spatial files (Shapefiles, GeoJSON)
Feature Specific Questions
What’s the difference between Tableau Desktop and Tableau Server?
Tableau Desktop is the authoring tool where you create visualizations and dashboards on your local computer. Tableau Server is the platform for sharing, distributing, and governing those visualizations across an organization. Desktop is for creation; Server is for collaboration and deployment.
Can Tableau handle large datasets?
Yes, Tableau can handle large datasets through several approaches:
- Live connections to data sources, leveraging database performance
- In-memory data extracts that compress data for faster analysis
- Data source filters to limit the data loaded
- Aggregation and sampling techniques for very large datasets
Performance depends on your hardware, data architecture, and how the visualizations are designed.
Does Tableau support real-time data?
Yes, Tableau supports real-time data through live connections to databases and APIs. For continuously updating dashboards, you can:
- Use live database connections
- Set automatic refresh intervals
- Implement Tableau’s Extract API for programmatic updates
- Leverage the Data Server for shared, centralized data sources
Can I embed Tableau dashboards in other applications?
Yes, Tableau offers several embedding options:
- Tableau JavaScript API for seamless integration
- Simple iframe embedding for basic needs
- Tableau Connected Apps for secure embedding
- Tableau Embedded Analytics for OEM partnerships
These options allow you to integrate Tableau visualizations into internal portals, customer-facing applications, or commercial products.
Pricing and Subscription FAQs
Is there a free version of Tableau?
Tableau Public is free but has limitations:
- All published visualizations are publicly accessible
- Cannot save work privately
- Limited data source connections
- 10GB storage limit
- No automated data refreshes
It’s ideal for students, hobbyists, journalists, and those wanting to showcase public data visualizations.
How is Tableau licensed?
Tableau uses role-based subscription licensing:
- Creators ($70/user/month) can connect to data and create content
- Explorers ($42/user/month) can use web authoring and modify existing content
- Viewers ($15/user/month) can interact with dashboards but not create or modify
These licenses apply to both Tableau Server (on-premises) and Tableau Online (cloud).
Does Tableau offer academic or nonprofit pricing?
Yes, Tableau offers special pricing programs:
- Academic programs provide free or discounted licenses to students and educators
- Nonprofit organizations receive discounts through the Tableau for Nonprofits program
- Tableau for Teaching allows instructors to use Tableau in classrooms at reduced rates
Details and eligibility requirements are available on Tableau’s website.
Support and Help FAQs
How can I get help with Tableau?
Tableau offers multiple support channels:
- Official documentation and knowledge base
- Community forums with active user participation
- Technical support via phone, email, or chat (for licensed users)
- Guided training programs (both free and paid)
- Partner network of certified consultants
- Annual conferences and user groups
How often is Tableau updated?
Tableau releases major updates quarterly, typically in March, June, September, and December. These updates include new features, performance improvements, and bug fixes. Maintenance releases for critical issues occur more frequently. Tableau Online (cloud) receives updates automatically, while Tableau Server requires manual updating.
Can I try Tableau before purchasing?
Yes, Tableau offers a 14-day free trial of Tableau Desktop with full functionality. For enterprise evaluations, Tableau also provides proof-of-concept programs where organizations can test Tableau Server or Tableau Online with guided assistance from Tableau representatives.
Conclusion: Is Tableau Worth It?
Summary of Tableau’s Strengths and Weaknesses
After a comprehensive review of Tableau’s capabilities, pricing, and user feedback, here’s a summary of its key strengths and weaknesses:
Strengths:
- 🌟 Industry-leading visualization capabilities that are both powerful and intuitive
- 🌟 Exceptional flexibility in connecting to almost any data source
- 🌟 Strong enterprise features for governance, security, and scaling
- 🌟 Regular innovation with quarterly updates adding valuable features
- 🌟 Extensive training resources and a supportive user community
- 🌟 Robust ecosystem of partners and integrations
- 🌟 Salesforce backing providing stability and resources
Weaknesses:
- ⚠️ Higher price point compared to some competitors, particularly for small organizations
- ⚠️ Steeper learning curve for advanced features and complex data modeling
- ⚠️ Mobile experience, while improving, isn’t as robust as the desktop version
- ⚠️ Performance can be challenged by extremely large or complex datasets
- ⚠️ Requires thoughtful implementation to avoid proliferation of unmanaged content
Final Recommendation and Verdict
Tableau stands as a premier data visualization and business intelligence platform that delivers exceptional value for organizations committed to becoming data-driven. Its combination of powerful analytics, intuitive interface, and enterprise readiness makes it a worthy investment for many scenarios.
Tableau is ideal for:
- Organizations with diverse and complex data sources that need unified analytics
- Companies willing to invest in analytics as a strategic capability
- Teams that prioritize visualization quality and analytical depth
- Enterprises requiring robust governance and security features
- Businesses looking for a mature, proven platform with strong support
Consider alternatives if:
- Your organization has very limited budget for analytics tools
- You need only basic reporting with minimal interactivity
- Your team is deeply embedded in Microsoft’s ecosystem (where Power BI may integrate better)
- You require specialized capabilities like associative analytics (where Qlik may excel)
The verdict? Tableau is worth the investment for organizations serious about extracting value from their data. While not the least expensive option, its combination of depth, flexibility, and usability delivers strong ROI through better decision-making, time savings, and data democratization.
As with any significant technology investment, success with Tableau depends not just on the software itself but on thoughtful implementation, user training, and creating a culture where data-driven decisions are valued. When these elements align, Tableau proves to be not just a visualization tool but a transformative platform for how organizations understand and use their data.